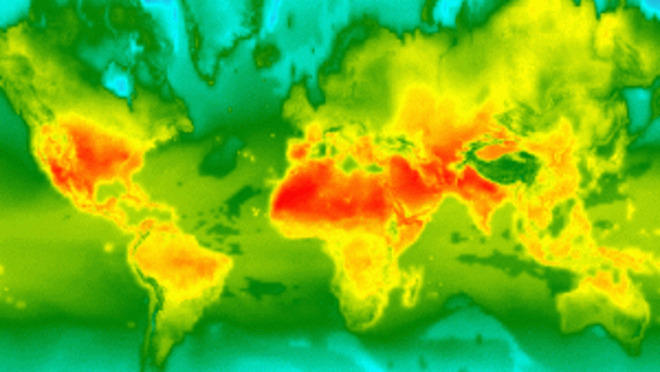
Regenerative agriculture Activities aim at mitigating negative consequences of farming activities, including erosion, depletion, pest invasions, desertification, salinization, decarbonization, chemical contamination, among others..

Detect issues that affect yield at an early stage Detecting issues at a later stage increases the risk of crop failure and yield losses. Fungus, Pests, Diseases Irrigation & Fertilization Issues Weeds Flooding & Drought

Onsite, Instant soil sampling to the farming community allowing them to have the results they require to carry on with their farming services. We focus at providing Nitrogen, Phosphate, Soil Organic carbon, co2, Phosphorus, PH, soil moisture.

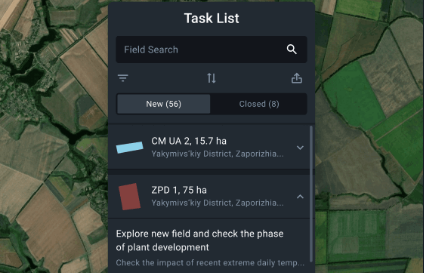
Monitor the state of your crops right from the office or home. Learn about the slightest changes on-the-spot, and make fast and reliable decisions on field treatment.

We sample the pattern of behavior over a rolling 6-day period to determine a baseline, this is then expressed on a scale of 1 -7 with 1 meaning low activity and 7 meaning extremely high.

to increase yields and decrease environmental impact. Using low-cost, in-field methods, water level, soil quality, and presence of pathogens and pests could be constantly monitored..

convert industrial side streams and recycled batteries into valuable circular economy products with a low carbon footprint..
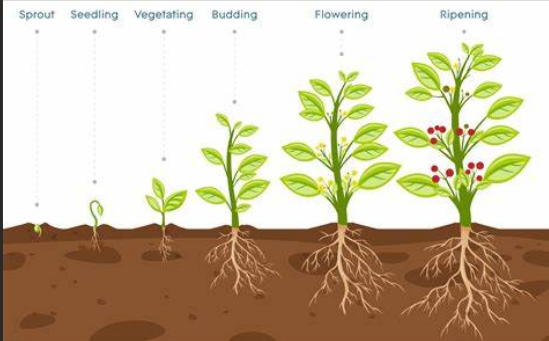
growth of a plant or crop or vegetable between germination and flowering.

Agriculture is responsible for nearly a quarter of methane emissions.

Solving forestry problems from space Monitor forest health remotely Get notified about any changes and risks Manage all your forest stands in one place. Forest fire monitoring based on NASA FIRMS abnormally high temperature alert technology Deforestation satellite monitoring within forest stands

Macro And Micro Nutrient Needs For Your Farming Needs. Foliar fertilizer containing zinc, manganese and sulphur extracted from recycled alkaline batteries.. Monitor your N _ P _ K and other important nutrients.

Optimization of water consumption in agriculture is necessary to preserve freshwater reserves and reduce the environment’s burden. Finding optimal irrigation and water resources for crops is necessary to increase the efficiency of water usage.

The crop water need mainly depends on: · the climate: in a sunny and hot climate crops need more water per day than in a cloudy and cool climate. EXAMPLE: maize and sugar cane will need more water than sorghum

Latest
We help farmers remotely assess the health of their crops, cut costs on scouting, soil testing, and farm management, and use seeds and fertilizers more efficiently.

Agriculture began independently in different parts of the globe, and included a diverse range of taxa. At least eleven separate regions of the Old and New World were involved as independent centers of origin. The development of agriculture about 12,000 years ago changed the way humans lived.

The changing global landscape combined with new and better data, technologies, and understanding means that agriculture can and must contribute to a wider range of development outcomes than ever before, including reducing poverty, ensuring adequate nutrition, creating strong food value chains, improving environmental sustainability, and promoting gender equity and equality..

Scientific agriculture is a broad multidisciplinary field of biology that encompasses the parts of exact, natural, economic and social sciences that are used in the practice and understanding of agriculture1. It includes the technologies of soil cultivation, crop cultivation and harvesting.